2020 has been the year to expect the unexpected. When building an investment thesis, few, if any, Private Equity firms would have predicted living in an economy that’s been rocked by a global pandemic.
With dry powder still at an all-time high, not only do firms need to manage threats related to economic uncertainties, but they must also safeguard against increased cyber risks.
Many data breaches are not disclosed due to fears surrounding the hit on reputation and lost credibility. Yet there is no doubt breaches are disrupting every industry, including Private Equity: In April of 2020, three British Private Equity firms were tricked into transferring $1.3 million into fraudulent bank accounts. And from February to April 2020, financial firms overall saw a 238% spike in cyberattacks. As proven by the cybersecurity statistics following the outbreak of COVID-19, executives must fully understand and prepare for:
- The reality of cyber risk in 2020
- The unexpected and long-term costs of a data breach
- The probability of cybersecurity issues affecting your business
The Reality of Cyber Risk in 2020
Hackers holding the ability to compromise – if not destroy – a business is nothing new. When looking at the impact of COVID-19 on technology, today’s remote workforce, combined with the opportunity to prey on the needs and fears of a pandemic, has made cyber risks more palpable than ever.
Protocols around remote work and cybersecurity are a necessity: The FBI has reported a 300% increase in cybercrime since the outbreak of COVID-19, and executives across all industries are feeling the effects. According to Carbon Black, 92% of U.S. businesses have seen increased cyber attacks in the past 12 months.
Cybersecurity is now the responsibility of all business leaders, including the c-suite and the board. In 2020 research by the Poneman Institute in partnership with IBM, it was revealed 1 in 4 people hold the CEO/COO responsible for cybersecurity policy and technology decisions.
Steve Durbin, Managing Director, Information Security Forum, shares with SmartBrief why CFOs also share the liability surrounding cyber risks: “A meticulous CFO can save the company the embarrassment and financial impact of a major breach by taking proactive steps in anticipation of targeted attacks…organizations of all sizes are so dependent upon technology and cyberspace to transact business that cybersecurity is now one of those critical areas requiring continued investment.”
Investors have also taken note of the increased cyber risks: PwC’s Global Investor Survey ranks cyber threats as the number one concern of investors.
When determining the priorities of daily business operations, the need to prioritize against cyber risk falls directly in the lap of leadership.
In partnership with the CIO or CTO, Private Equity executives must take the lead on cybersecurity to safeguard their intellectual property, dry powder, and portfolio companies. This includes prioritizing cybersecurity policies and procedures, ensuring protective measures are implemented and building a human firewall by educating employees on the new and evolving risks.
As outlined below, firms who don’t acknowledge this responsibility risk damaging their portfolio’s value through lost business decreased credibility, and a multitude of both direct and intangible costs.
The unexpected and long-term cost of a data breach
According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, the 2020 average cost of a data breach in the United States is ~$8.64 million. Taking a closer look at the costs based on the size of a company’s database, the average cost of a data breach per record is $150.
For the financial industry, the cost of a data breach is nearly double at ~$5.85 million.
When quantifying the financial impact of a cyber breach, there are immediate and somewhat expected costs surrounding a breach. These include paying ransom fees, upgrades or improvements to the cybersecurity governance, and paying for a technical investigation to uncover and solve the source of the problem.
However, the consequences of a data breach go beyond technology, tunneling straight to the core of business operations.
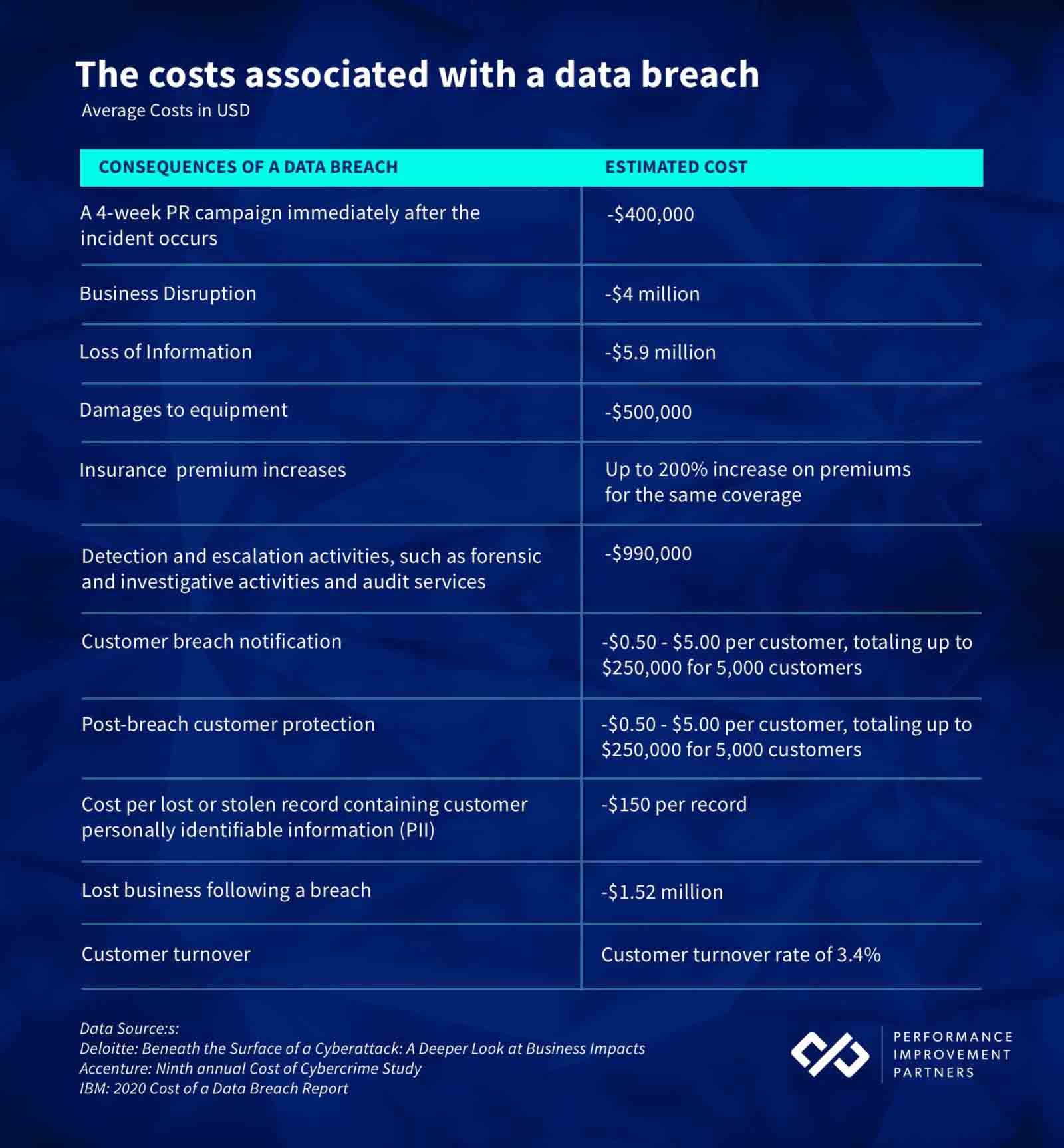
When considering the average data breach costs, it’s important to note the less-obvious intangible costs. Examples, as identified by Deloitte’s Beneath the Surface of a Cyberattack report, include:
- Devaluation of trade name
- The impact of operational disruption
- Increased cost to raise debt
- The lost value of customer relationships
- Insurance premium increases
- The value of lost contract revenue
Consider the fact that, according to PwC, 87% of consumers will take their business elsewhere if they don’t trust the company is responsibly handling their data.
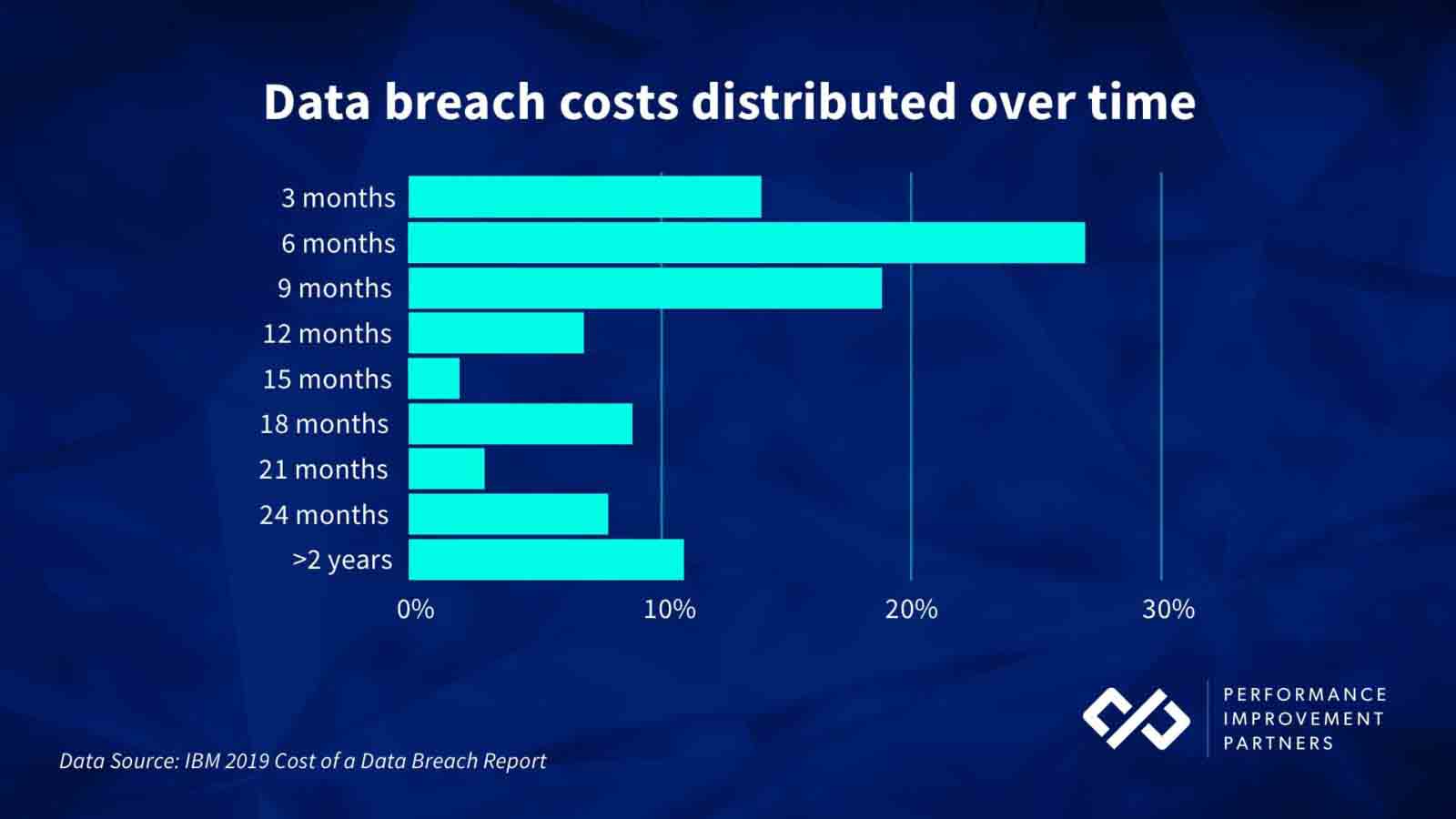
Factors such as this have a negative financial impact on a business years after the breach occurs. As illustrated in 2019 research by IBM, one-third of data breach costs are incurred more than a year after it occurs.
Planning for prevention: How a cyber incident response plan results in cost savings
When considering the value of cybersecurity spend, the advantages of risk mitigation have a direct impact on the bottom line.
According to IBM’s 2020 Report, cybersecurity investments result in the following financial benefits:
- Companies with an incident response team and extensive testing of response plans save $2 million
- Businesses who have fully deployed security automation, such as the use of artificial intelligence platforms, saved an average of $3.58 million over those with no security automation
- Working with a managed security services provider results in cost mitigation of $78,054
Learn more about how to plan for prevention by utilizing the Defense-in-Depth (DiD) approach to cybersecurity.
Cyber Risk Management: The Probability of Cybersecurity Issues Affecting Your Business
Now more than ever, the likelihood of a cybersecurity issue affecting your business is real. As cited by The World Economic Forum, 68% of business leaders believe the cybersecurity threats to their company are increasing.
In serving the cybersecurity needs of Private Equity firms, Performance Improvement Partners has experienced client demand that correlates with these findings. In H1 of 2020, compared to H1 of 2019, there was a 750% increase in portfolio-wide cyber initiatives, in addition to doubling the number of cyber engagements.
Cybersecurity threats to the finance industry
When taking a deeper look at the finance industry, it’s unmistakable the cybersecurity threats are greater than that the average industry. Not only is the cost of a data breach almost $2 million above the average, 52% of all attacks in March of 2020 were finance related.
Fred Purdue, Infrastructure Practice Manager of Performance Improvement Partners, shares with Business Insider why Private Equity in particular needs to take notice of the increased cyber threats:
“If you’re a CEO, there might be a 5% chance that you’re going to have a significant cybersecurity event this year. There’s a 100% chance the head of sales is going to come in and complain about Salesforce tomorrow. If you’re a Private Equity firm and you own 20 of those companies that has a 5% risk each, you have a certainty that you’re going to have a significant type of attack.”
The following image demonstrates the path from cyber attack to cyber breach, and the likelihood of the average middle-market Private Equity firm to experiencing an attack, incident, exploit, and breach.
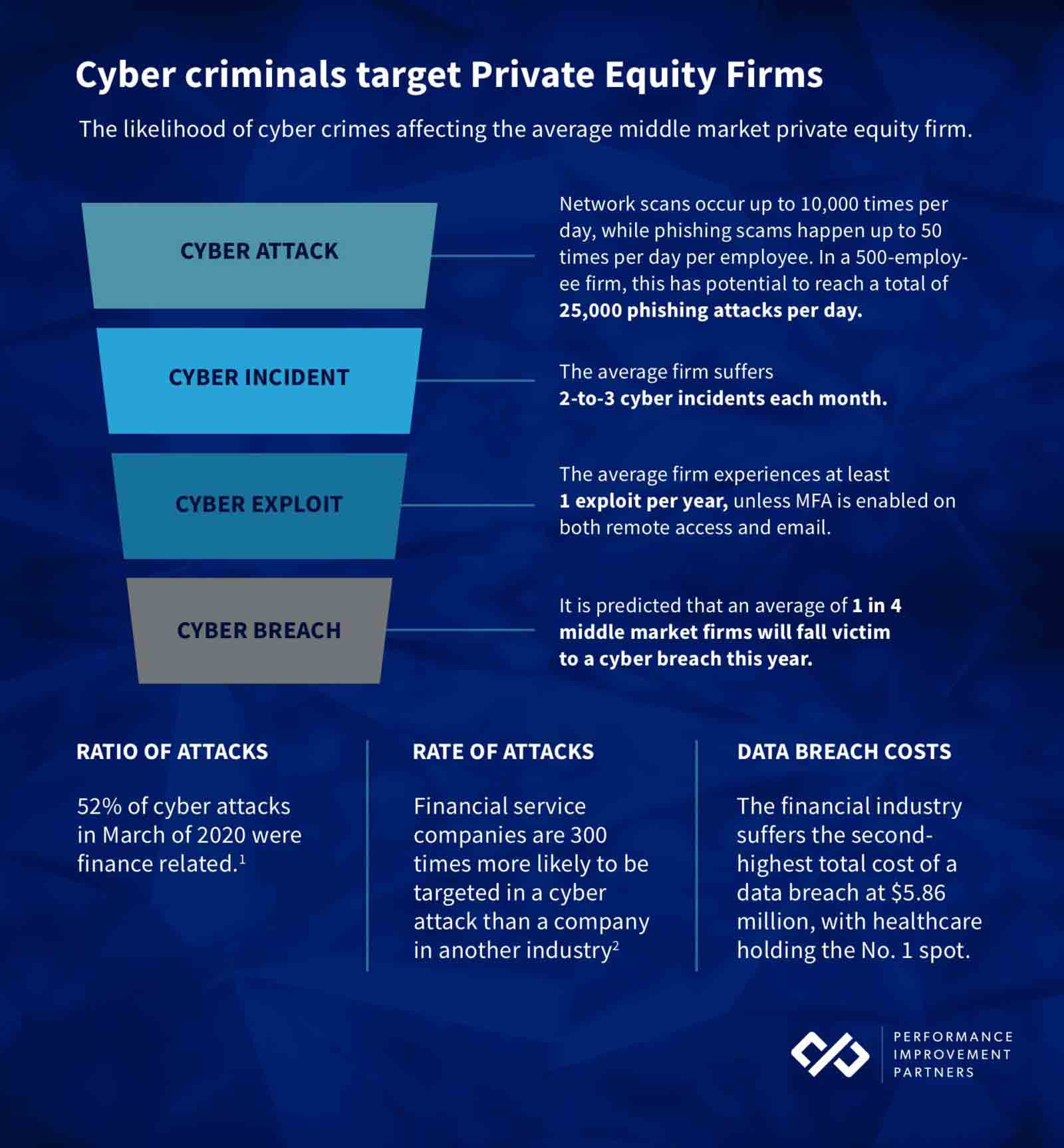
As demonstrated in the image, it is predicted that an average of 1 in 4 middle-market firms will fall victim to a data breach this year.
These breaches originate with the 2-to-3 cyber incidents experienced each month, which often go undetected.
Firms with the ability to quickly detect cyber threats reap the financial rewards: When a breach lifecycle is over 200 days, the average cost is an additional $1.12 million than breaches with a lifecycle under 200 days.
Overcome cybersecurity challenges and mitigate financial risk
In tackling the challenges around cybersecurity, there are numerous tactics companies can take to safeguard business continuity: Find out how to protect your firm and your portfolio with the 2020 Private Equity Guide to Cybersecurity.
Insights include the most overlooked source of cyber attacks, the hidden risks surrounding most cyber insurance policies, and what actions leadership – including the C-Suite and Board – are taking to protect investments.
Get the PE Cybersecurity Guide Now!



